Imagine a world where cyber defenses are not just reactive, but predictive—where your systems can detect threats before they happen, and security protocols evolve faster than hackers can adapt. Welcome to the era of generative AI cybersecurity. As digital landscapes grow increasingly complex and cyber threats become more cunning, traditional security measures are no longer enough. Enter generative AI—a ground-breaking technology capable of creating, learning, and adapting in ways that mimic human intelligence, but at machine speed.
This powerful innovation is revolutionizing cybersecurity by automating threat detection, generating real-time responses, and simulating attacks to uncover hidden vulnerabilities. But with great power comes great responsibility. The same tools that protect can also be weaponized. In this article, we explore the dual-edged sword of generative AI: the cutting-edge innovations enhancing digital defense, and the emerging risks that could redefine the future of cyber warfare. Generative AI Training
The Rise of Generative AI in Cybersecurity
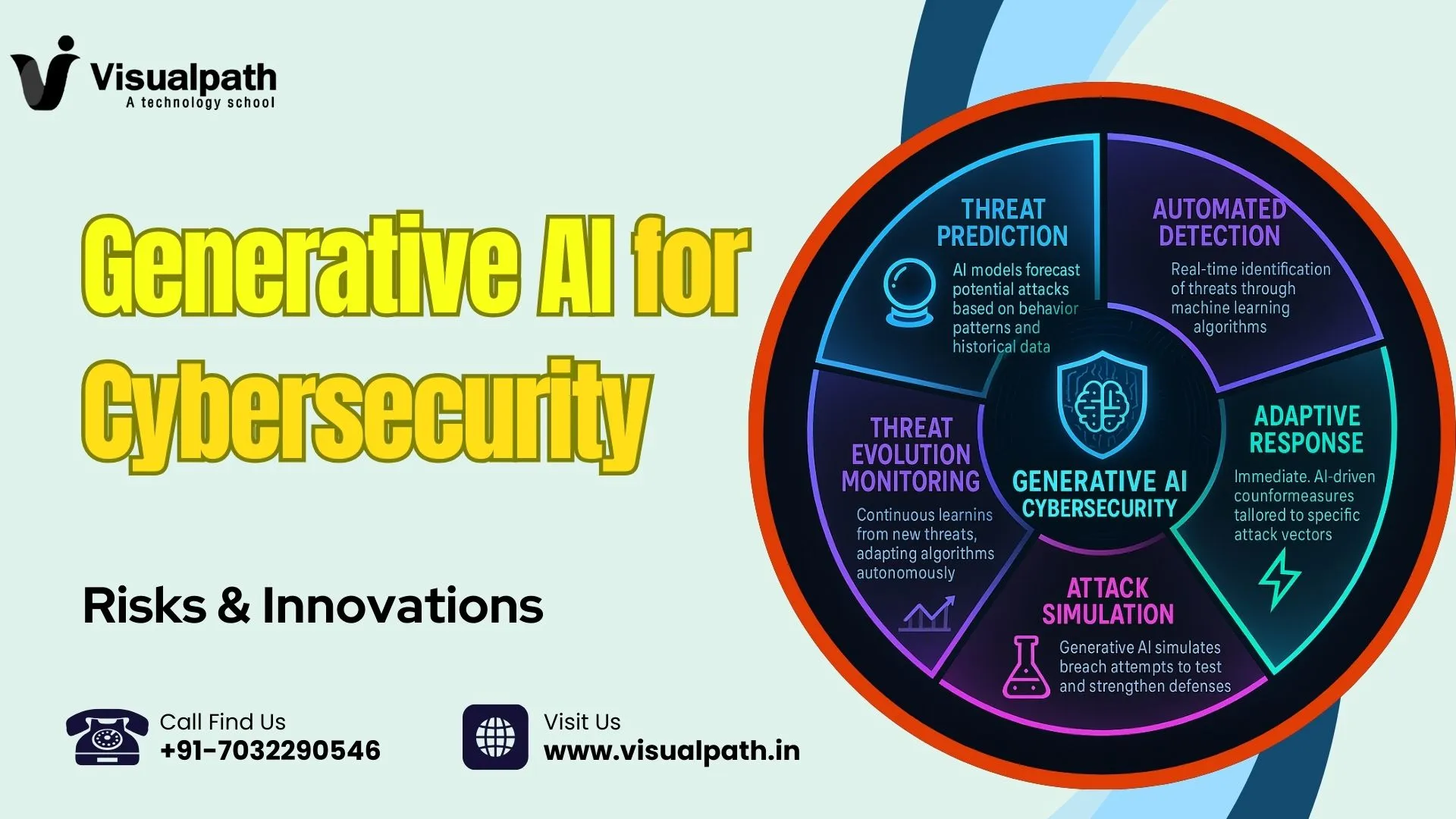
Generative AI cybersecurity tools are revolutionizing how we detect and respond to threats. These tools can simulate attack scenarios, generate malware signatures, and even predict future cyberattack strategies. As a result, security teams are better equipped to pre-emptively defend their systems. One of the key applications of generative AI is in automated threat detection, where AI models analyze vast datasets to identify patterns indicative of potential breaches. GenAI Online Training
In addition, AI threat detection has improved incident response times, reducing the window in which attackers can exploit vulnerabilities. This innovation allows for real-time decision-making and a proactive approach to digital defense.
Key Innovations Driving Change
Several innovations are propelling generative AI cybersecurity to the forefront. For example, the development of AI-driven penetration testing tools enables organizations to continuously test their infrastructure for weaknesses without the need for constant human intervention. These tools not only identify vulnerabilities but also suggest remediation tactics.
Another significant innovation is in the area of zero trust architecture, where generative AI assists in validating every access request based on context and behaviour. This ensures that only authorized users gain access, dramatically reducing the risk of insider threats or compromised credentials.
Risks of Generative AI in Cybersecurity
While the benefits are substantial, the risks associated with generative AI cybersecurity cannot be ignored. One of the most pressing concerns is the use of generative AI by malicious actors to create convincing phishing emails, deepfake videos, and synthetic identities. These AI-generated threats can bypass traditional security filters and deceive even the most cautious users. Gen
Moreover, the AI-generated malware can evolve autonomously, making it more difficult for traditional antivirus software to keep up. This self-modifying behaviour means that malware can adapt in real-time, evading detection and increasing the likelihood of successful attacks.
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
With great power comes great responsibility. The use of generative AI in cybersecurity raises several ethical and regulatory issues. There is a growing need for AI governance frameworks that ensure AI is used responsibly. These frameworks must address concerns such as bias in AI decision-making, transparency of AI algorithms, and the accountability of AI-driven actions.
Incorporating generative AI into cybersecurity strategies must also comply with existing data protection laws such as GDPR and CCPA. Organizations need to strike a balance between leveraging AI capabilities and maintaining the privacy and security of user data. Generative AI Course Curriculum
Future Outlook and Strategic Recommendations
Looking forward, the future of generative AI cybersecurity is both promising and complex. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into cybersecurity will deepen, leading to more intelligent and adaptive security systems. However, the dual-use nature of generative AI means that ongoing vigilance is required to mitigate risks.
To effectively harness generative AI, organizations should invest in AI literacy among cybersecurity teams, implement robust monitoring systems, and collaborate with cybersecurity experts to tailor AI solutions to their specific needs. Emphasizing continuous learning and adaptation will be key in staying ahead of cyber threats.
Conclusion
Generative AI cybersecurity is redefining the boundaries of what’s possible in digital defense. While it brings powerful tools to the table, it also introduces complex challenges that require careful management. By understanding both the risks and innovations, organizations can leverage this technology to create safer, smarter, and more resilient digital environments.
Trending Courses: Artificial Intelligence, Data Science with Generative AI, Cyber Security
Visualpath stands out as the leading and best institute for software online training in Hyderabad. We provide Generative AI Courses Online. You will get the best course at an affordable cost.
Call/What’s App – +91-7032290546Visit: https://www.visualpath.in/generative-ai-course-online-training.html